Subscribe now and get the latest podcast releases delivered straight to your inbox.
Google rolls out BERT update to provide more nuanced search results

Oct 31, 2019

In November of 2018, Google rolled out a new tool to help searchers find exactly what they were looking for. Google called it Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, or BERT for short. According to Google, this update impacts 10% of search queries and is meant to make up for the fact that computers and algorithms don't understand nuance and context the same way that people do.
Last week, Google rolled out a major BERT update:
"With the latest advancements from our research team in the science of language understanding — made possible by machine learning — we’re making a significant improvement to how we understand queries, representing the biggest leap forward in the past five years, and one of the biggest leaps forward in the history of Search."
What is BERT?
BERT is a natural language processing (NLP) software system that can contextualize a search query based on the words a user puts in the search bar.
The result is that you get search results that are more accurate for your query. At the same time, you help Google and its algorithm perform better by helping Google understand your search intent when you use a keyword phrase instead of just one keyword.
Google has open-sourced BERT, which means anyone can use BERT to create their own system of answering questions. As people continue to use BERT, the program will become more intelligent and will be able to properly contextualize search queries to deliver users with the best content on the web surrounding any given topic.
According to Google, BERT represents "the biggest leap forward in the last five years" and "one of the biggest leaps forward in the history of search."
BERT's impact on search rankings
Specifically, BERT is making an impact on search rankings and featured snippets. As you probably know all too well, anytime Google makes a major change in its algorithm or introduces a new tool, webpages may experience a drop in rankings. BERT is no exception.
Pages that are sloppy or unhelpful will most likely see drops in their rankings. This is because BERT is designed to improve how the search algorithm understands context. When a page doesn't match the context in a specific search query, Google assumes that the page is unhelpful. If you see drops in traffic over the next few weeks, it could be from BERT.
On the flip side, pages that use keywords appropriately and provide good, accurate content will likely see a jump in their rankings. This is usually the case in any Google update.
Websites that are committed to producing and publishing high-quality, well-researched pieces of content will end up on top, while scammy websites and those that only have superficial content will fall in rankings.
BERT-enhanced search results
BERT allows users to use their normal language when searching. As Google points out, searchers often don't know what keywords to use because they're coming to search to find information. With BERT, you can type in your question or query without knowing the exact keywords and still find what you're looking for.
What this means for publishers and writers is that content can be more conversational without risking losing rankings. Keywords are still important, as always, but you don't need to use keywords in an unnatural way. Featured snippets should be geared toward how people ask questions naturally.
For searchers, BERT means that Google can pick up on subtle, but important, nuances in your search query to deliver you the best results even when you don't know what keywords to use.
An example Google uses to illustrate this point is the query "2019 Brazil traveler to USA need a visa." The keyword here is "to." Before BERT, Google wouldn't have recognized "to" as crucial to searcher intent and, therefore, the results would have been more likely to miss the mark.
Now, BERT helps Google understand that "to" in this search indicates that someone is traveling from Brazil to the US and wants to know if they need to get a visa. The results are now more useful for the searcher.
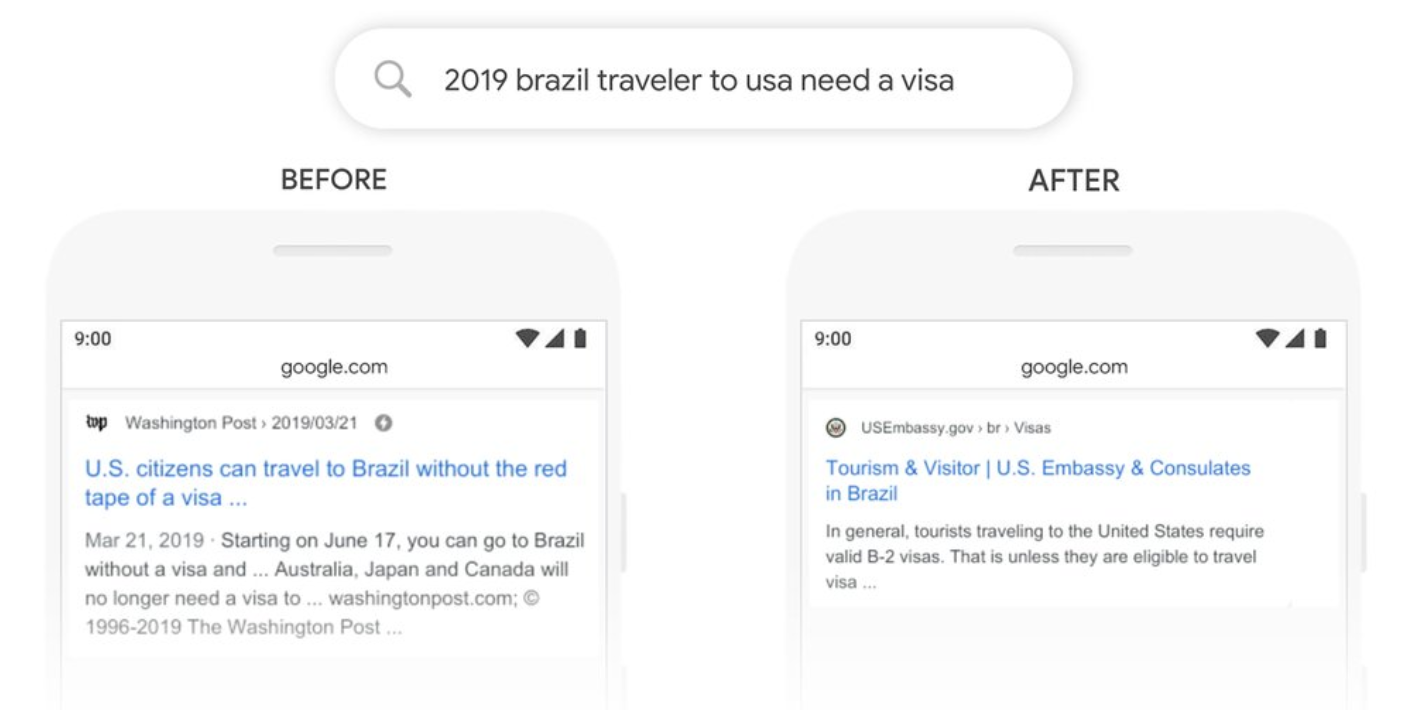 (Source: Google)
(Source: Google)
Or, for another example, consider these side-by-side results for the same search query:
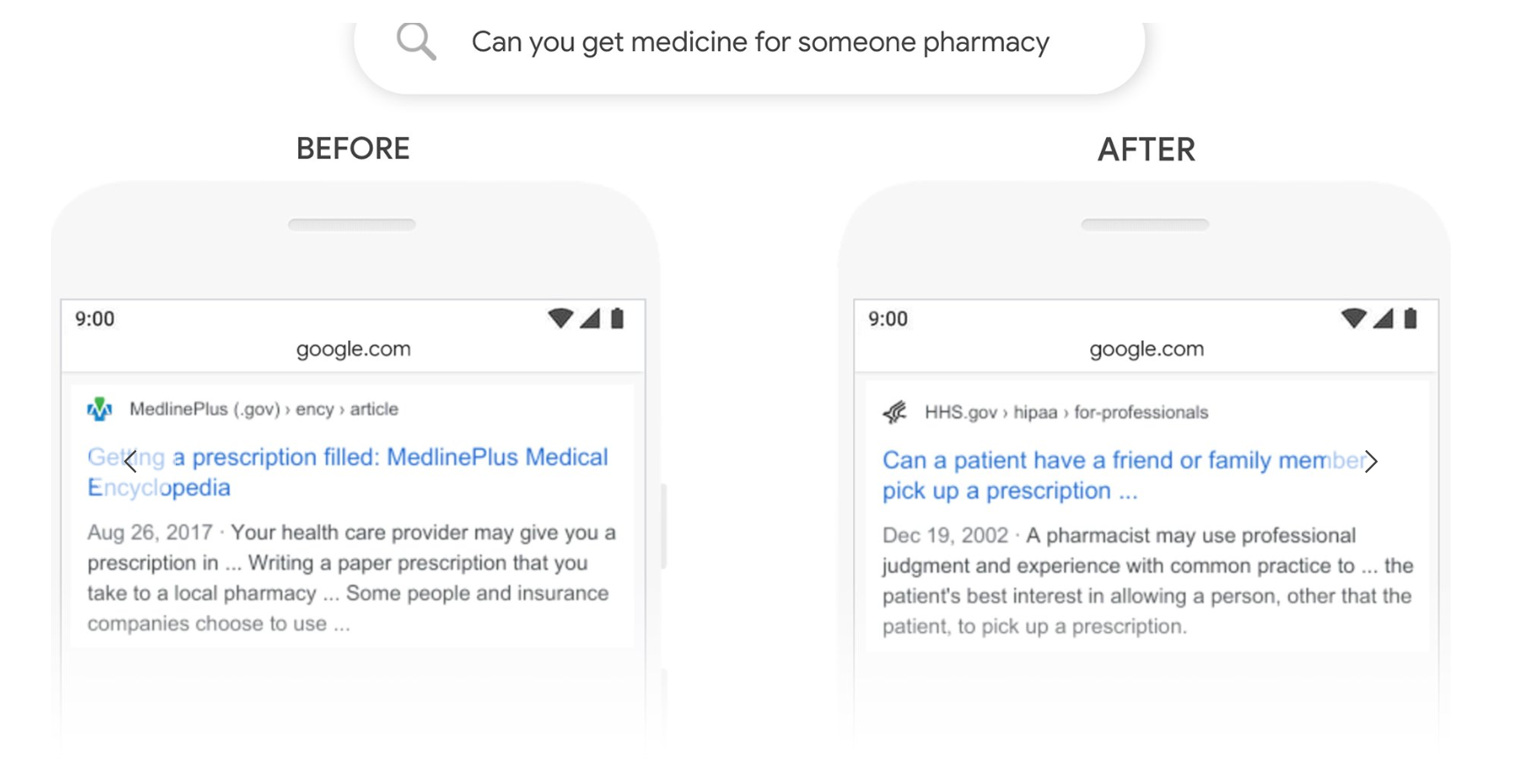 (Source: Google)
(Source: Google)
Google taking BERT worldwide
BERT was initially introduced for US-based searches. Google has since rolled it out worldwide and is using the information it learns from US searches to inform search results in other parts of the world.
The same is true for featured snippets. So far, BERT has been put in place for featured snippets in 12 countries. To date, Google reports seeing improved results for featured snippets in Korean, Hindi, and Portuguese.
Google acknowledges that BERT isn't a solution for every search and admits that even with this powerful NLP technology, searchers will still be able to "stump" Google's algorithm.
For marketers, writers, and publishers, this update is a reminder that the best way to improve your rankings and give your audience the information it's looking for is by providing accurate content that's rich in details and answers the questions your searchers are asking.
Free: Assessment